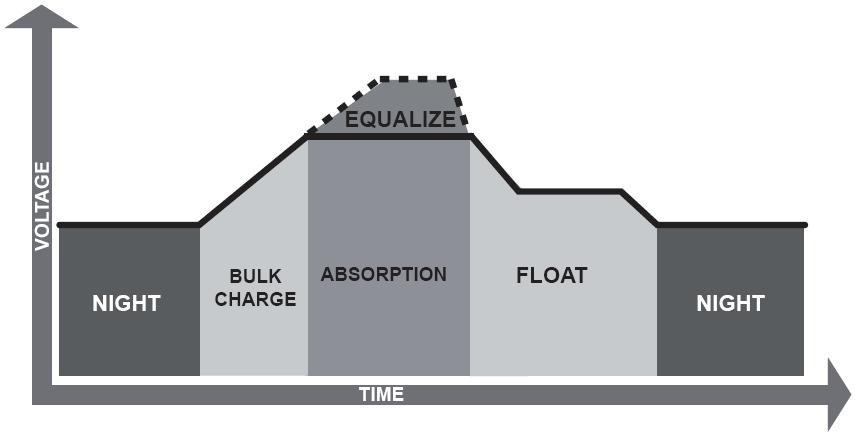
Battery charging takes place in 3 basic stages: Bulk, Absorption, and Float.
Bulk Charge: The first stage of battery charging.
Current is sent to batteries at the maximum safe rate they will accept until voltage rises to near (80-90%) full charge level. Voltages at this stage typically range from 10.5 volts to 15 volts. There is no “correct” voltage for bulk charging, but there may be limits on the maximum current that the battery and/or wiring can take.
Absorption Charge: The 2nd stage battery charging.
Voltage remains constant and current gradually tapers off as internal resistance increases during charging. It is during this stage that the charger puts out maximum voltage. Voltages at this stage are typically around 14.2 to 15.5 volts. (The internal resistance gradually goes up because there is less and less to be converted back to normal full charge).
Float Charge: The 3rd stage of battery charging.
After batteries reach full charge, charging voltage is reduced to a lower level (typically 12.8 to 13.2) to reduce gassing and prolong battery life. This is often referred to as a maintenance or trickle charge, since it’s main purpose is to keep an already charged battery from discharging. PWM, or “pulse width modulation” accomplishes the same thing. In PWM, the controller or charger senses tiny voltage drops in the battery and sends very short charging cycles (pulses) to the battery. This may occur several hundred times per minute. It is called “pulse width” because the width of the pulses may vary from a few microseconds to several seconds. Note that for long term float service, such as backup power systems that are seldom discharged, the float voltage should be around 13.02 to 13.20 volts.
Chargers: Most garage and consumer (automotive) type battery chargers are bulk charge only, and have little (if any) voltage regulation. They are fine for a quick boost to low batteries, but not to leave on for long periods. Among the regulated chargers, there are the voltage regulated ones, which keep a constant regulated voltage on the batteries. If these are set to the correct voltages for your batteries, they will keep the batteries charged without damage. These are sometimes called “taper charge” – as if that is a selling point. What taper charge really means is that as the battery gets charged up, the voltage goes up, so the amps out of the charger goes down. They charge OK, but a charger rated at 20 amps may only be supplying 5 amps when the batteries are 80% charged. To get around this, some companies have come out with “smart”, or multi-stage chargers. These use a variable voltage to keep the charging amps much more constant for faster charging.
Key to achieving long battery life is to ensure you are using high quality controllers, chargers or inverters that support the above methods.
Bulk Charge: The first stage of battery charging.
Current is sent to batteries at the maximum safe rate they will accept until voltage rises to near (80-90%) full charge level. Voltages at this stage typically range from 10.5 volts to 15 volts. There is no “correct” voltage for bulk charging, but there may be limits on the maximum current that the battery and/or wiring can take.
Absorption Charge: The 2nd stage battery charging.
Voltage remains constant and current gradually tapers off as internal resistance increases during charging. It is during this stage that the charger puts out maximum voltage. Voltages at this stage are typically around 14.2 to 15.5 volts. (The internal resistance gradually goes up because there is less and less to be converted back to normal full charge).
Float Charge: The 3rd stage of battery charging.
After batteries reach full charge, charging voltage is reduced to a lower level (typically 12.8 to 13.2) to reduce gassing and prolong battery life. This is often referred to as a maintenance or trickle charge, since it’s main purpose is to keep an already charged battery from discharging. PWM, or “pulse width modulation” accomplishes the same thing. In PWM, the controller or charger senses tiny voltage drops in the battery and sends very short charging cycles (pulses) to the battery. This may occur several hundred times per minute. It is called “pulse width” because the width of the pulses may vary from a few microseconds to several seconds. Note that for long term float service, such as backup power systems that are seldom discharged, the float voltage should be around 13.02 to 13.20 volts.
Chargers: Most garage and consumer (automotive) type battery chargers are bulk charge only, and have little (if any) voltage regulation. They are fine for a quick boost to low batteries, but not to leave on for long periods. Among the regulated chargers, there are the voltage regulated ones, which keep a constant regulated voltage on the batteries. If these are set to the correct voltages for your batteries, they will keep the batteries charged without damage. These are sometimes called “taper charge” – as if that is a selling point. What taper charge really means is that as the battery gets charged up, the voltage goes up, so the amps out of the charger goes down. They charge OK, but a charger rated at 20 amps may only be supplying 5 amps when the batteries are 80% charged. To get around this, some companies have come out with “smart”, or multi-stage chargers. These use a variable voltage to keep the charging amps much more constant for faster charging.
Key to achieving long battery life is to ensure you are using high quality controllers, chargers or inverters that support the above methods.